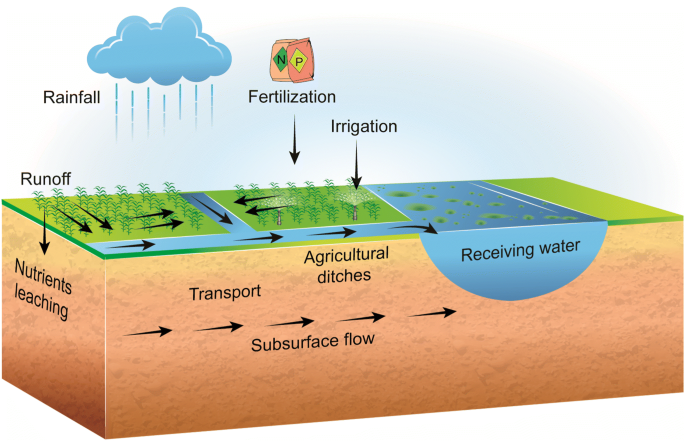
Have you ever considered how the fertilizers used in agriculture might be affecting the quality of water in nearby streams, rivers, or lakes? The relationship between farming practices and water quality is a topic of growing concern, especially when you consider the balance needed to maintain healthy water bodies and productive agricultural lands.
Understanding NBOD and Its Significance
NBOD, or Nitrogenous Biochemical Oxygen Demand, is a measure of how much oxygen is consumed in the aquatic environment due to the presence of nitrogen-containing compounds. These compounds often originate from fertilizers, manure, and agricultural runoff. Understanding NBOD is crucial, as it impacts aquatic ecosystems, potentially leading to oxygen depletion, which can harm fish and other aquatic life.
What is NBOD?
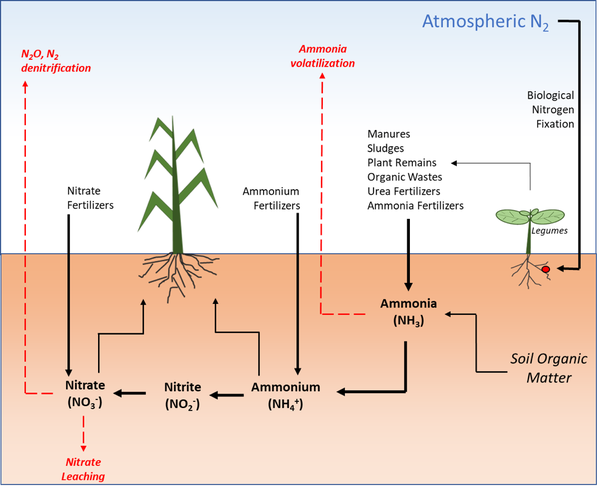
NBOD refers to the amount of oxygen needed to oxidize nitrogenous compounds in water. This demand for oxygen is crucial since it indicates how much nitrogen from agricultural sources is entering water bodies. High NBOD levels can lead to hypoxic conditions, which are detrimental to aquatic life.
Why is NBOD Important for Water Quality?
NBOD is a key parameter for determining water quality because it reflects the burden of nitrogen compounds introduced into water systems. Elevated NBOD levels can cause oxygen depletion, affecting aquatic organisms’ survival, growth, and reproduction. When oxygen levels drop too low, it can create “dead zones” where aquatic life struggles to survive.
The Role of Fertilizers in NBOD Levels
Fertilizers, while essential for modern agriculture, are a primary source of the nitrogen compounds that contribute to NBOD. Understanding how fertilizers affect NBOD levels helps in devising strategies to minimize their negative impact on water quality.
How Fertilizers Contribute to NBOD
Fertilizers used in agriculture often contain nitrogen in the form of nitrates and ammonium. When these fertilizers are applied to fields, not all of the nitrogen is absorbed by the crops. The excess nitrogen can leach into the groundwater or be carried by surface runoff to nearby water bodies, where it contributes to NBOD.
Impacts of Excessive Fertilizer Use
Excessive use of fertilizers can lead to nutrient pollution in water bodies. This nutrient enrichment facilitates the growth of algae, which upon decomposition, increases the demand for oxygen in the water, further elevating NBOD levels. This nutrient-overload situation is often termed eutrophication, which is harmful to aquatic ecosystems.
Balancing Fertilizer Use for Sustainable Agriculture
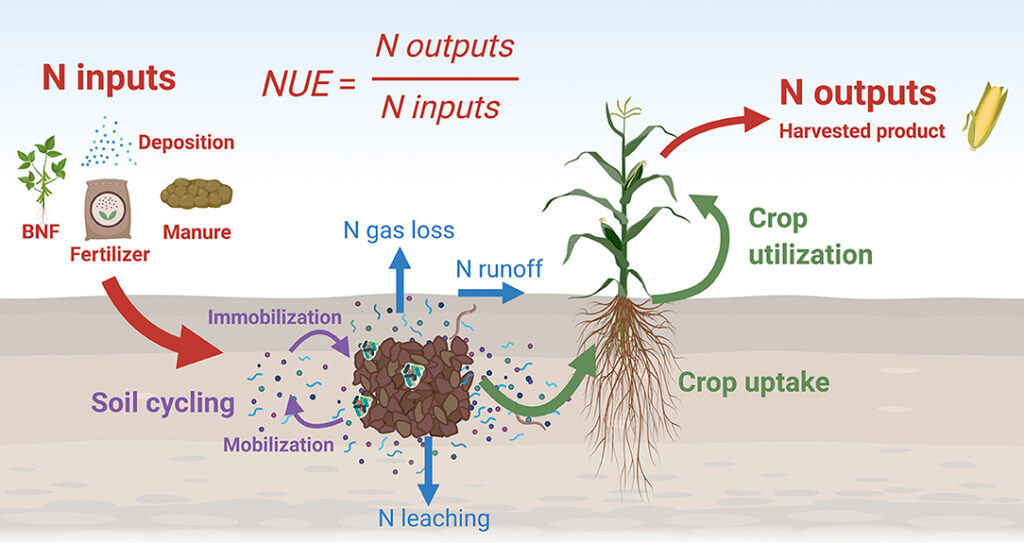
The challenge lies in achieving a balance where sufficient fertilizers are used to ensure crop productivity but not at the expense of degrading water quality. This balance is not only essential for the sustainability of agriculture but also for maintaining healthy aquatic ecosystems.
Best Practices for Fertilizer Application
Implementing best practices in fertilizer application can significantly reduce the impact on NBOD. These include using the right type of fertilizer, applying it at the right time, and at the correct amount. Precision agriculture techniques, such as soil testing and crop monitoring, can aid in determining the precise fertilizer needs.
Role of Technology in Reducing NBOD Impact
Technology plays a crucial role in managing fertilizer use. Tools like GPS-guided tractors and drones equipped with sensors help in applying fertilizers more accurately. These technologies ensure that fertilizers are only applied where needed, reducing runoff and subsequent nitrogen leaching into water bodies.
Evaluating Water Quality: Measuring NBOD
Monitoring NBOD is critical for assessing the health of water bodies impacted by agricultural runoff. Regular measurement allows for timely intervention and management strategies to prevent ecological degradation.
Methods of Measuring NBOD
There are various methods to measure NBOD, ranging from simple field tests to complex laboratory analyses. Field kits can provide quick NBOD assessments, while laboratory analysis offers detailed insights into the nitrogen content and its potential oxygen demand.
Importance of Regular Monitoring
Regular monitoring of NBOD is vital to understand trends and identify areas at risk of high nitrogen pollution. This data helps in adjusting agricultural practices to mitigate negative impacts and aids in policy-making for environmental protection.
Implementing Policy Measures
Policy measures play a significant role in balancing agricultural needs and environmental health. Effective policies can guide the agricultural community in adopting sustainable practices that minimize NBOD impact.
Current Policies on Fertilizer Use
Many governments have implemented policies regulating the use of fertilizers to protect water bodies. These policies include restrictions on the type and amount of fertilizer, application times, and standards for water quality maintenance.
Future Directions for Policy Development
Future policies may focus on incentivizing sustainable practices, funding research in alternative fertilization methods, and promoting community engagement in water quality conservation efforts. Policymakers must balance agricultural productivity with environmental sustainability to ensure the long-term health of our ecosystems.
Community and Farmer Engagement
Community and farmer involvement is crucial for successful implementation of sustainable practices. Education and awareness can empower these stakeholders to take an active role in protecting water quality.
Educating Farmers on Sustainable Practices
Extension services and agricultural workshops can provide farmers with the knowledge and tools they need to reduce the impact of fertilizers on NBOD levels. Engaging with farmers through workshops, demonstrations, and collaborative projects ensures they are equipped to adopt best practices.
Role of Community Participation in Conservation
Communities can participate in conservation efforts through monitoring initiatives and advocating for better water management practices. Their involvement ensures a comprehensive approach to safeguarding water quality and creating sustainable agricultural landscapes.
Conclusion
Striving for a balance between fertilizer use and water quality is essential for the health of our ecosystems. By understanding the impact of agricultural practices on NBOD levels, you can take informed steps to protect water sources. Through a combination of best practices in fertilizer application, technological advancements, policy support, and community involvement, the goal of sustainable agriculture and clean water can be achieved. This shared responsibility ensures a future where agriculture thrives alongside vibrant and healthy water ecosystems.