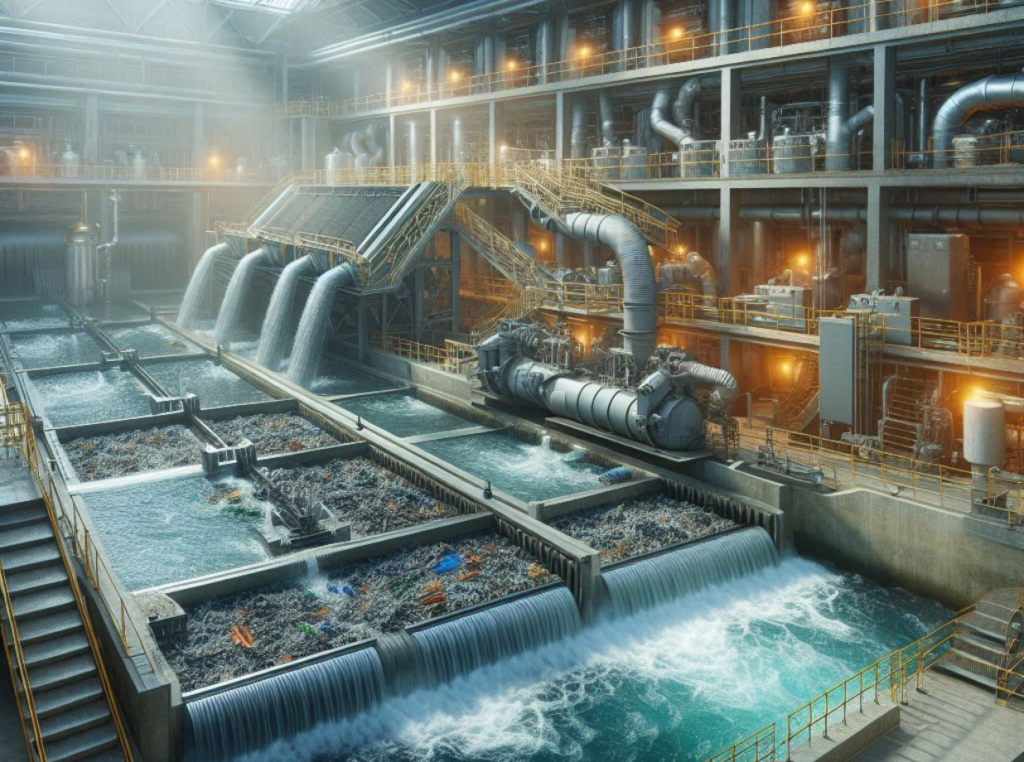
Have you ever wondered what happens to wastewater after you flush the toilet or let water go down the drain? It’s a fascinating process that starts with an essential phase known as preliminary treatment. Understanding this stage of wastewater management provides insight into how we maintain public health, protect the environment, and conserve water resources.

The Role of Preliminary Treatment
Preliminary treatment is the initial step in the comprehensive process of wastewater management. This stage serves as the frontline defense, filtering out large debris that could damage downstream equipment or clog pipes. Everything from sticks, rags, and plastics to more unexpected items can find their way into the wastewater system. By removing these large objects early, the process becomes more manageable and efficient.
Why is Preliminary Treatment Important?
In wastewater treatment, preliminary treatment is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it prevents damage and blockages in the treatment plant’s machinery, saving on potential repair costs and downtime. Secondly, it creates a more efficient environment for subsequent treatment stages, enhancing overall effectiveness.
Key Benefits:
| Benefits | Description |
|---|---|
| Protecting Equipment | Safeguards machinery from large, damaging debris |
| Improving Efficiency | Ensures smoother operation and increases the efficacy of later stages |
| Reducing Costs | Minimizes repair and replacement expenses |
| Environmental Protection | Keeps harmful objects out of the water system |
The Headworks: Where It All Begins
At the centerpiece of preliminary treatment lies the headworks. This is the entry point of influent wastewater at a treatment plant. Equipped with various apparatus designed to screen and remove large debris, the headworks play a pivotal role in safeguarding downstream processes from potential harm.
The Apparatus of Preliminary Treatment
Several critical components make up the preliminary treatment stage. Each type of apparatus is designed for a specific function, ensuring the removal of different kinds of debris. Here, we break down these components and their unique roles.
Bar Screens
Bar screens are the first line of defense in preliminary treatment. These screens consist of parallel bars placed a couple of inches apart to trap large objects while allowing water to pass through.
Types of Bar Screens:
- Manual Bar Screens: Operated by hand and typically used in small plants or as backup systems.
- Mechanical Bar Screens: Automated and efficient, used in larger facilities for continuous operation.
Grit Chambers
Next in line are grit chambers, which remove inorganic particles like sand, gravel, and small stones. These particles could cause significant wear and tear on the plant’s machinery if not removed early in the process.
Types of Grit Chambers:
- Horizontal Flow Grit Chambers: Wastewater flows horizontally, allowing grit to settle at the bottom.
- Aerated Grit Chambers: Air is pumped in to ensure grit settles while organic matter remains suspended.
- Cyclonic Grit Chambers: Use centrifugal forces to separate grit from the wastewater.
Comminutors and Grinders
Comminutors and grinders break down larger pieces of debris into smaller particles. These machines ensure that any leftover materials do not disrupt the following stages of wastewater treatment.
Key Advantages:
- Reduction in Size: Converts large particles into manageable sizes.
- Improved Flow: Prevents blockages in pipes and downstream equipment.
Flow Equalization
Flow equalization basins serve to moderate the flow of wastewater entering the treatment plant. This ensures that downstream processes receive a consistent volume and composition of influent, improving efficiency and performance.
Flow Equalization Techniques:
- Storage Basins: Hold excess flow during peak times and release it during low-flow periods.
- Variable Speed Pumps: Adjust the rate of flow based on real-time data.
Screenings Handling Equipment
The debris collected during preliminary treatment needs proper disposal. Screenings handling equipment ensures that collected material is hygienically removed from the site and disposed of in an environmentally friendly manner.
Common Equipment:
- Conveyors: Transport debris to disposal points.
- Compactors: Reduce the volume of collected screenings for easier handling.
The Process, Step-by-Step
Step 1: Influent Entry
When wastewater enters the treatment plant, it immediately encounters the bar screens. Large debris is screened out and collected for disposal, setting the stage for smoother operations down the line.
Step 2: Grit Removal
The wastewater then flows into the grit chambers, where heavier inorganic materials settle to the bottom. This process mitigates the wearing effects gritty particles could have on mechanical equipment.
Step 3: Size Reduction
Comminutors and grinders come into play to break down any remaining large particles, ensuring that subsequent treatments can operate effectively.
Step 4: Flow Regulation
Finally, the wastewater is transported to flow equalization basins. Here, the influent is held and released at a controlled rate, ensuring a consistent flow into the primary treatment stage.
The Environmental Impact of Preliminary Treatment
By efficiently removing large debris and inorganic matter, preliminary treatment plays a crucial role in minimizing environmental harm. It ensures that subsequent treatment stages can focus on removing smaller and often more harmful contaminants like bacteria, viruses, and chemical pollutants.
Reducing Pollutants
When large debris is effectively removed during preliminary treatment, it reduces the overall pollutant load entering natural water bodies. This is crucial in maintaining aquatic ecosystem health.
Protecting Aquatic Life
Large debris can cause significant harm to aquatic life if not removed from wastewater. Fish, birds, and other wildlife can ingest these items, leading to injury or death.
Modern Innovations in Preliminary Treatment
Technological advancements have led to more efficient and robust preliminary treatment processes. Here are some modern innovations making waves in the wastewater industry:
Advanced Screening Systems
Advanced screening systems use sophisticated technology to improve the efficiency of debris removal. For example, fine screens can capture smaller particles that traditional bar screens might miss.
Smart Sensors and Controls
With the advent of IoT (Internet of Things), smart sensors and control systems enhance the monitoring and automation of preliminary treatment processes. These systems can adjust operations in real-time for optimal efficiency.
Benefits of Smart Systems:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Immediate updates and alerts.
- Automated Adjustments: Instant changes based on data.
- Energy Efficiency: Reduces power consumption through optimal operations.
The Challenges and Solutions
Preliminary treatment is not without its challenges. However, understanding these issues allows for the development of effective solutions.
Debris Overload
One of the primary challenges is managing large volumes of debris during peak times. This can overwhelm bar screens and other preliminary treatment equipment.
Solutions:
- Increased Capacity: Install additional bar screens or larger grit chambers.
- Flow Equalization: Use flow equalization basins to manage peak flows effectively.
Equipment Wear and Tear
The abrasive nature of grit and inorganic materials can lead to rapid wear and tear of equipment.
Solutions:
- Durable Materials: Use high-quality, wear-resistant materials for equipment.
- Regular Maintenance: Implement a rigorous maintenance schedule to mitigate wear.
Energy Consumption
Preliminary treatment processes can be energy-intensive, contributing to operational costs and environmental impact.
Solutions:
- Energy-Efficient Equipment: Invest in machinery designed for low energy consumption.
- Solar Power: Utilize renewable energy sources to offset power usage.
Regulatory Standards and Compliance
Compliance with regulatory standards ensures that preliminary treatment processes are up-to-date and effective. Adhering to these regulations is crucial for the legal and environmental standing of a treatment facility.
Common Regulations
- EPA Guidelines: The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) sets stringent guidelines for wastewater treatment processes.
- Local Code: Municipalities may have additional requirements that treatment plants must meet.
How to Stay Compliant
- Regular Audits: Conduct frequent internal audits to ensure compliance.
- Training: Keep staff trained and informed about current regulations.
- Documentation: Maintain meticulous records of processes and maintenance activities.
Future Trends in Preliminary Treatment
Looking forward, the preliminary treatment stage is poised for further advancements. These future trends promise to enhance efficiency and effectiveness even further.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI can provide predictive analytics to optimize the operation of preliminary treatment systems. Through machine learning algorithms, AI can predict when screens will need cleaning or when grit chambers will require emptying.
Waste-to-Energy Technologies
Some modern treatment plants are beginning to use collected debris as a resource. Waste-to-energy technologies can convert organic waste into biogas, providing a renewable energy source for the plant.
Remote Monitoring and Control
Advancements in remote monitoring allow operators to oversee operations from anywhere in the world. This ensures rapid response times and increased operational flexibility.
How You Can Contribute
You might think that wastewater management is entirely out of your hands, but there are steps you can take to support these processes:
Reduce Debris
Minimize what you flush or pour down drains. Items like wet wipes, paper towels, and plastics should never go into the wastewater system.
Proper Disposal
Dispose of hazardous materials properly. Chemicals, oils, and medications can severely affect the treatment process.
Educate Others
Spread awareness about the importance of proper wastewater management. Inform your family, friends, and community about what can and cannot go down the drain.
Support Sustainable Practices
Advocate for and support policies that promote effective wastewater management and the use of renewable energy in treatment plants.
Conclusion
Understanding preliminary treatment in wastewater management offers an enlightening glimpse into the crucial steps that protect our water systems. This initial phase, starting at the headworks, removes large debris and sets the stage for more detailed purification processes. From bar screens and grit chambers to advanced screening systems and smart sensors, each component plays an integral role in ensuring the efficiency and effectiveness of wastewater treatment.
By reducing pollutants, protecting the environment, and supporting the overall function of the treatment facility, preliminary treatment is the unsung hero of modern sanitation and hygiene. As we look toward future trends and innovations, one thing remains clear: effective preliminary treatment is fundamental to the sustainability of our water resources and the well-being of our communities.
Feel empowered to act, whether by reducing your own waste or advocating for advanced treatment technologies. Together, we can ensure a cleaner, safer, and more sustainable future for all.
Additional Resources
- EPA – Municipal Wastewater: Comprehensive information on municipal wastewater treatment, including preliminary treatment processes.
- Water Environment Federation – Collection Systems: Resources on wastewater collection systems, which are closely related to preliminary treatment.
- International Water Association – Preliminary Treatment of Wastewater: An educational resource specifically focused on preliminary treatment processes.
- Water Online – Preliminary Treatment: Articles and insights on preliminary treatment technologies and practices.
- AWWA – Wastewater Treatment 101 (PDF): A comprehensive guide that includes information on preliminary treatment as part of the overall wastewater treatment process.
- ScienceDirect – Wastewater Treatment: Academic articles and research papers on various aspects of wastewater treatment, including preliminary processes.
- Global Water Intelligence – Preliminary Treatment: Market insights and technology updates related to preliminary treatment in the water industry.
